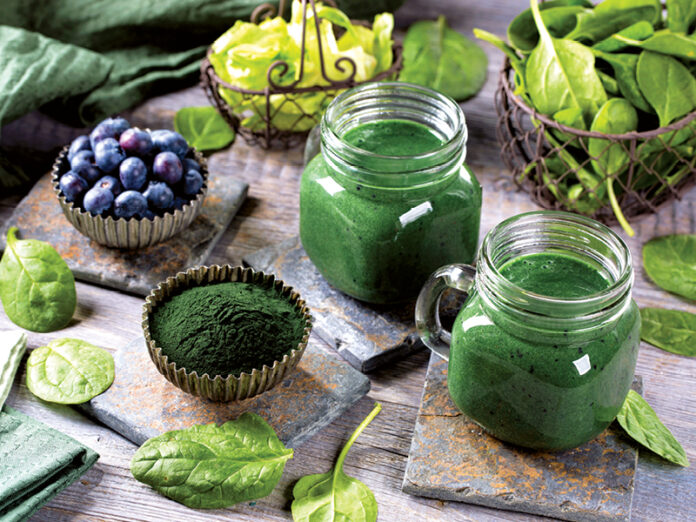
Inflammation is useful when our bodies respond to immediate stress, such as infection, injury or allergies. But chronic inflammation can be a path to chronic disease, including arthritis, tendinitis, bursitis, celiac disease, heart disease, diabetes and more. While some foods we eat promote inflammation, others suppress it. Here are seven food types that fight inflammation to prevent or manage many of these conditions.
-
- Anti-Oxidant Rich Fruits & Vegetables: Foods such as kale, broccoli, spinach, strawberries, blueberries, raspberries are rich in antioxidants.
- Monounsaturated-Rich Nuts: Almonds and pecans, which are rich in monounsaturated fats and vitamin E are often associated with a reduction in bodily inflammation.
- Omega 3-rich Nuts/Seeds: Walnuts, chia seeds and flax seeds are all rich in omega-3 fatty acids and other components which may contribute anti-inflammatory effects.
- Legumes: Chickpeas, lentils and beans are among the richest available sources of dietary fibre and magnesium, two nutrients that are highly associated with reduction in bodily inflammation.
- Olive Oil: Diets rich in olive oil (3-4 Tbsp. a day) are associated with the reduction in biochemical markers of inflammation.
- Whole Grains: Steel cut oats, 100% whole grain bread or pasta, quinoa, brown rice are anti-inflammatory, in part because they do not excessively raise blood sugar (compared to white bread, instant oats, sugary cereals and white rice). I include sweet potatoes in this group.
- Others: Turmeric, cinnamon, green tea, coffee, soy, ginger, garlic and cocoa are foods that may all have anti-inflammatory effects on our bodies.
Myth Busted
Contrary to popular belief, there is no strong evidence to suggest that nightshade vegetables (potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, eggplants) cause or worsen inflammation in humans. These are healthy, nutrient-rich foods that should not be avoided if you enjoy them.